Redis-存储底层数据结构-ziplist的优化
ziplist的缺点
我们都知道ziplist的插入效率其实是$o(n)$的,redis的解决方案是ziplist不可太长。使用到ziplist的两个上层数据结构分别是dict和zset,其二者有配置hash-max-ziplist-entries和zset-max-ziplist-entries来限制其在底层存储是ziplist状态下的长度。
同时我们在这里解释了ziplist递归更新的风险,这将短时间阻塞主线程,带来尖刺现象。
我们可以来看看redis针对递归更新的优化。
listpack的优化
针对ziplist的连锁更新风险,设计了一种新的数据结构,优化掉了ziplist中的prvelen。
存储结构
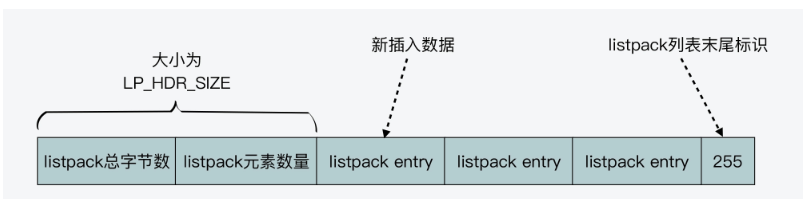
这个我们可以从lpNew中看出来。
1 | |
主要就是set listpack的总字节数,listpack的元素数量,列表尾标识。
如何解决递归扩容问题
接着我们需要看看entry是如何设计来解决掉prvelen的。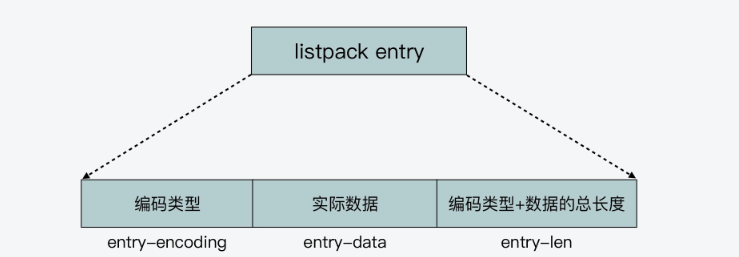
在 listpack 中,因为每个列表项只记录自己的长度,而不会像 ziplist 中的列表项那样,会记录前一项的长度。所以,当我们在 listpack 中新增或修改元素时,实际上只会涉及每个列表项自己的操作,而不会影响后续列表项的长度变化,这就避免了连锁更新。
如何做查询?
listpack也是同时支持正向和逆向查询。这里我们可以看看lpSeek方法。他的注释就写了怎么正向seek和逆向seek。
1 | |
- 然后接着判断如果numele如果不是没有指定的话,那么就判断逆向扫描是否是更优解。
- 然后最下面的逻辑就是正向扫描和逆向扫描
- 正向扫描先判断是否lp是否有entry,这个具体的逻辑在
ipFirst中,接着就开始往后遍历。 - 接着就就逆向扫描逻辑。
接下来主要是分析分析最后的正向遍历和逆向遍历1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61unsigned char *lpFirst(unsigned char *lp) {
lp += LP_HDR_SIZE; /* Skip the header. */
if (lp[0] == LP_EOF) return NULL;
return lp;
}
unsigned char *lpNext(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *p) {
((void) lp); /* lp is not used for now. However lpPrev() uses it. */
p = lpSkip(p);
if (p[0] == LP_EOF) return NULL;
return p;
}
unsigned char *lpSkip(unsigned char *p) {
// 1. 先调用lpCurrentEncodedSize,获取p的编码长度+数据长度
// 2. 获取最后的总长度,然后跳过这个元素
unsigned long entrylen = lpCurrentEncodedSize(p);
entrylen += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,entrylen);
p += entrylen;
return p;
}
/* Return the encoded length of the listpack element pointed by 'p'. If the
* element encoding is wrong then 0 is returned. */
uint32_t lpCurrentEncodedSize(unsigned char *p) {
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_7BIT_UINT(p[0])) return 1;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_6BIT_STR(p[0])) return 1+LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR_LEN(p);
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_13BIT_INT(p[0])) return 2;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_16BIT_INT(p[0])) return 3;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_24BIT_INT(p[0])) return 4;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_INT(p[0])) return 5;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_64BIT_INT(p[0])) return 9;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_12BIT_STR(p[0])) return 2+LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR_LEN(p);
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_STR(p[0])) return 5+LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR_LEN(p);
if (p[0] == LP_EOF) return 1;
return 0;
}
/* Store a reverse-encoded variable length field, representing the length
* of the previous element of size 'l', in the target buffer 'buf'.
* The function returns the number of bytes used to encode it, from
* 1 to 5. If 'buf' is NULL the function just returns the number of bytes
* needed in order to encode the backlen. */
unsigned long lpEncodeBacklen(unsigned char *buf, uint64_t l) {
if (l <= 127) {
//.......
return 1;
} else if (l < 16383) {
//.......
return 2;
} else if (l < 2097151) {
//.......
return 3;
} else if (l < 268435455) {
//.......
return 4;
} else {
//.......
return 5;
}
}
正向的逻辑比较简单。
- 主要逻辑集中在
lpSkip,然后调用了lpCurrentEncodedSize和lpEncodeBacklen。 lpCurrentEncodedSize,获取当前的编码类型+实际数据的长度。lpEncodeBacklen根据这个获取表示前面的entrylen总长度所需字节数,即最开始数据结构图的entry-len。- 获取初偏移量之后就可以向后偏移了。
逆向的逻辑。
1 | |
- 在lpLast中,先找到尾节点,然后调用lpPrev。
- lpPrev则先判断是否是最开头的节点,否则p–,然后获取长度,最后回到当前节点的起始字节位置。
接下来我们需要看看lpDecodeBacklen函数。
1 | |
从这个函数的角度,我们可以很明白其是如何利用最后的entry-len来表示长度的,其利用1xxxxxxx表示开头,其他的都是0xxxxxxx, 也就是entry-len整体呈现1xxxxxxx 0xxxxxxx 0xxxxxxx.....。
到这里我们大概就知道其insert是如何做的了,估计应该就是将插入点后的entry后移,插入新entry即可。
所以接着我们来看看是如何做insert的。
如何做insert?
方法注释拿过来看看
1 | |
大致意思是将ele插到p的前面,后面或者代替p,其是通过where来选择。newP则被设置刚添加元素的地址。如果是删除操作,newP则是写一个entry的位置,如果p已经是最后一个元素了,则set为null。返回值是新的lp的地址。
接下来看看具体的函数逻辑。
- 首先是一些前置的处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
unsigned char intenc[LP_MAX_INT_ENCODING_LEN];
unsigned char backlen[LP_MAX_BACKLEN_SIZE];
uint64_t enclen; /* The length of the encoded element. */
if (ele == NULL) where = LP_REPLACE;
if (where == LP_AFTER) {
p = lpSkip(p);
where = LP_BEFORE;
}
unsigned long poff = p-lp;
- intenc用于存储编码后的整数。
- backlen用于存储
entry-len的长度,不过是小端法。 - enclen用于保存p所需长度,包括编码类型和具体长度。
- 接着就是一些对where的特殊处理以及获得p offset。
- 接着如果是整数,就将ele解析intenc中,长度解析到enclen。主要逻辑在
lpEncodeGetType中,整体逻辑相对简单,这里不做过多分析。如果ele是null,则代表p是需要删除的。
接下来主要是分析下整数和字符串在listpack中是如何存储的,相信有前面的ziplist这里应该很好理解了。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67int enctype;
if (ele) {
enctype = lpEncodeGetType(ele,size,intenc,&enclen);
} else {
enctype = -1;
enclen = 0;
}
int lpEncodeGetType(unsigned char *ele, uint32_t size, unsigned char *intenc, uint64_t *enclen) {
int64_t v;
if (lpStringToInt64((const char*)ele, size, &v)) {
if (v >= 0 && v <= 127) {
/* Single byte 0-127 integer. */
intenc[0] = v;
*enclen = 1;
} else if (v >= -4096 && v <= 4095) {
/* 13 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<13)+v;
intenc[0] = (v>>8)|LP_ENCODING_13BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
*enclen = 2;
} else if (v >= -32768 && v <= 32767) {
/* 16 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<16)+v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_16BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
intenc[2] = v>>8;
*enclen = 3;
} else if (v >= -8388608 && v <= 8388607) {
/* 24 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<24)+v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_24BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
intenc[2] = (v>>8)&0xff;
intenc[3] = v>>16;
*enclen = 4;
} else if (v >= -2147483648 && v <= 2147483647) {
/* 32 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<32)+v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_32BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
intenc[2] = (v>>8)&0xff;
intenc[3] = (v>>16)&0xff;
intenc[4] = v>>24;
*enclen = 5;
} else {
/* 64 bit integer. */
uint64_t uv = v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_64BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = uv&0xff;
intenc[2] = (uv>>8)&0xff;
intenc[3] = (uv>>16)&0xff;
intenc[4] = (uv>>24)&0xff;
intenc[5] = (uv>>32)&0xff;
intenc[6] = (uv>>40)&0xff;
intenc[7] = (uv>>48)&0xff;
intenc[8] = uv>>56;
*enclen = 9;
}
return LP_ENCODING_INT;
} else {
if (size < 64) *enclen = 1+size;
else if (size < 4096) *enclen = 2+size;
else *enclen = 5+size;
return LP_ENCODING_STRING;
}
}
整数的存储这个倒是很好理解,对于整数,总共有6种类型,这是他们开始的标识符。接着的内存就存储具体的内容。当然除了LP_ENCODING_7BIT_UINT,他是0xxxxxxx,就足以表示7位无符号整数了。
1 | |
字符串的存储, 也是通过一个标识符号,以上对应字节来存储长度。通过lpEncodeGetType我们很容易得知,
LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR -> 10xxxxxx,后面6位表示长度,最大长度63
LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR -> 1110xxxx xxxxxxxx, 后面12位置表示长度,最大长度4095
LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR -> 11110000 xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx,后32位表示长度,最大长度$2^{32}-1$。正好对应lpEncodeGetType中的else逻辑
1 | |
接下来是一些变量的获取,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33// 将enclen解析到backlen中
unsigned long backlen_size = ele ? lpEncodeBacklen(backlen,enclen) : 0;
// lp的长度
uint64_t old_listpack_bytes = lpGetTotalBytes(lp);
// 获取保存p所需的字节数。
uint32_t replaced_len = 0;
if (where == LP_REPLACE) {
// 获取encoding类型+data的字节数
replaced_len = lpCurrentEncodedSize(p);
// 获取保存entry-len所需字节数
replaced_len += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,replaced_len);
}
// 获取new_listpack_bytes,旧长度 + p的编码类型和数据保存所需长度 + p的entry-len - p的长度(如果p需要被replace)。
uint64_t new_listpack_bytes = old_listpack_bytes + enclen + backlen_size
- replaced_len;
if (new_listpack_bytes > UINT32_MAX) return NULL;
/* Return the encoded length of the listpack element pointed by 'p'. If the
* element encoding is wrong then 0 is returned. */
uint32_t lpCurrentEncodedSize(unsigned char *p) {
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_7BIT_UINT(p[0])) return 1;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_6BIT_STR(p[0])) return 1+LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR_LEN(p);
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_13BIT_INT(p[0])) return 2;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_16BIT_INT(p[0])) return 3;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_24BIT_INT(p[0])) return 4;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_INT(p[0])) return 5;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_64BIT_INT(p[0])) return 9;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_12BIT_STR(p[0])) return 2+LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR_LEN(p);
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_STR(p[0])) return 5+LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR_LEN(p);
if (p[0] == LP_EOF) return 1;
return 0;
}接下来就是具体的更新操作了。== LP_BEFORE,将
- 如果where== LP_BEFORE,将
p-tail这一段向后移动enclen+backlen_size。 - 否则where == LP_REPLACE, 这个时候将p的后一个节点->tail后移
(enclen+backlen_size)-replaced_len即可。
- 如果where== LP_BEFORE,将
接着判断
new_listpack_bytes < old_listpack_bytes,则缩小空间,并将dst指向ele保存的地址下面的逻辑就是个newP赋值,
接着是将ele的内容拷贝到dst中,先拷贝
encoding+data,再拷贝entry-len。最后就是update一下listpack的num和totalbytes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72/* Realloc before: we need more room. */
if (new_listpack_bytes > old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
/* Setup the listpack relocating the elements to make the exact room
* we need to store the new one. */
if (where == LP_BEFORE) {
memmove(dst+enclen+backlen_size,dst,old_listpack_bytes-poff);
} else { /* LP_REPLACE. */
long lendiff = (enclen+backlen_size)-replaced_len;
memmove(dst+replaced_len+lendiff,
dst+replaced_len,
old_listpack_bytes-poff-replaced_len);
}
/* Realloc after: we need to free space. */
if (new_listpack_bytes < old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
/* Store the entry. */
if (newp) {
*newp = dst;
/* In case of deletion, set 'newp' to NULL if the next element is
* the EOF element. */
if (!ele && dst[0] == LP_EOF) *newp = NULL;
}
if (ele) {
if (enctype == LP_ENCODING_INT) {
memcpy(dst,intenc,enclen);
} else {
lpEncodeString(dst,ele,size);
}
dst += enclen;
memcpy(dst,backlen,backlen_size);
dst += backlen_size;
}
/* Update header. */
if (where != LP_REPLACE || ele == NULL) {
uint32_t num_elements = lpGetNumElements(lp);
if (num_elements != LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN) {
if (ele)
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements+1);
else
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements-1);
}
}
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,new_listpack_bytes);
#if 0
/* This code path is normally disabled: what it does is to force listpack
* to return *always* a new pointer after performing some modification to
* the listpack, even if the previous allocation was enough. This is useful
* in order to spot bugs in code using listpacks: by doing so we can find
* if the caller forgets to set the new pointer where the listpack reference
* is stored, after an update. */
unsigned char *oldlp = lp;
lp = lp_malloc(new_listpack_bytes);
memcpy(lp,oldlp,new_listpack_bytes);
if (newp) {
unsigned long offset = (*newp)-oldlp;
*newp = lp + offset;
}
/* Make sure the old allocation contains garbage. */
memset(oldlp,'A',new_listpack_bytes);
lp_free(oldlp);
#endif
return lp;
listpack已经成功的将连锁更新给优化掉了,也就是插入只需要更新一次内存。